In descriptive statistics, a subject plot or boxplot (additionally known as a subject and whisker plot) is a form of chart sometimes utilized in explanatory data analysis. Discipline plots visually current the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages.
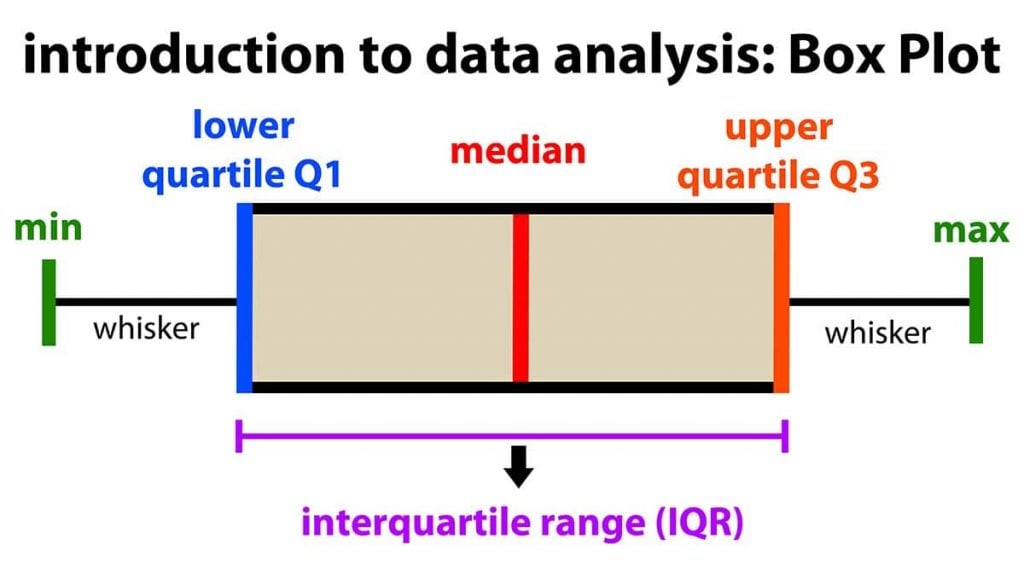
Discipline plots current the five-number summary of a set of knowledge: along with the minimal score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (larger) quartile, and most score.
Definitions
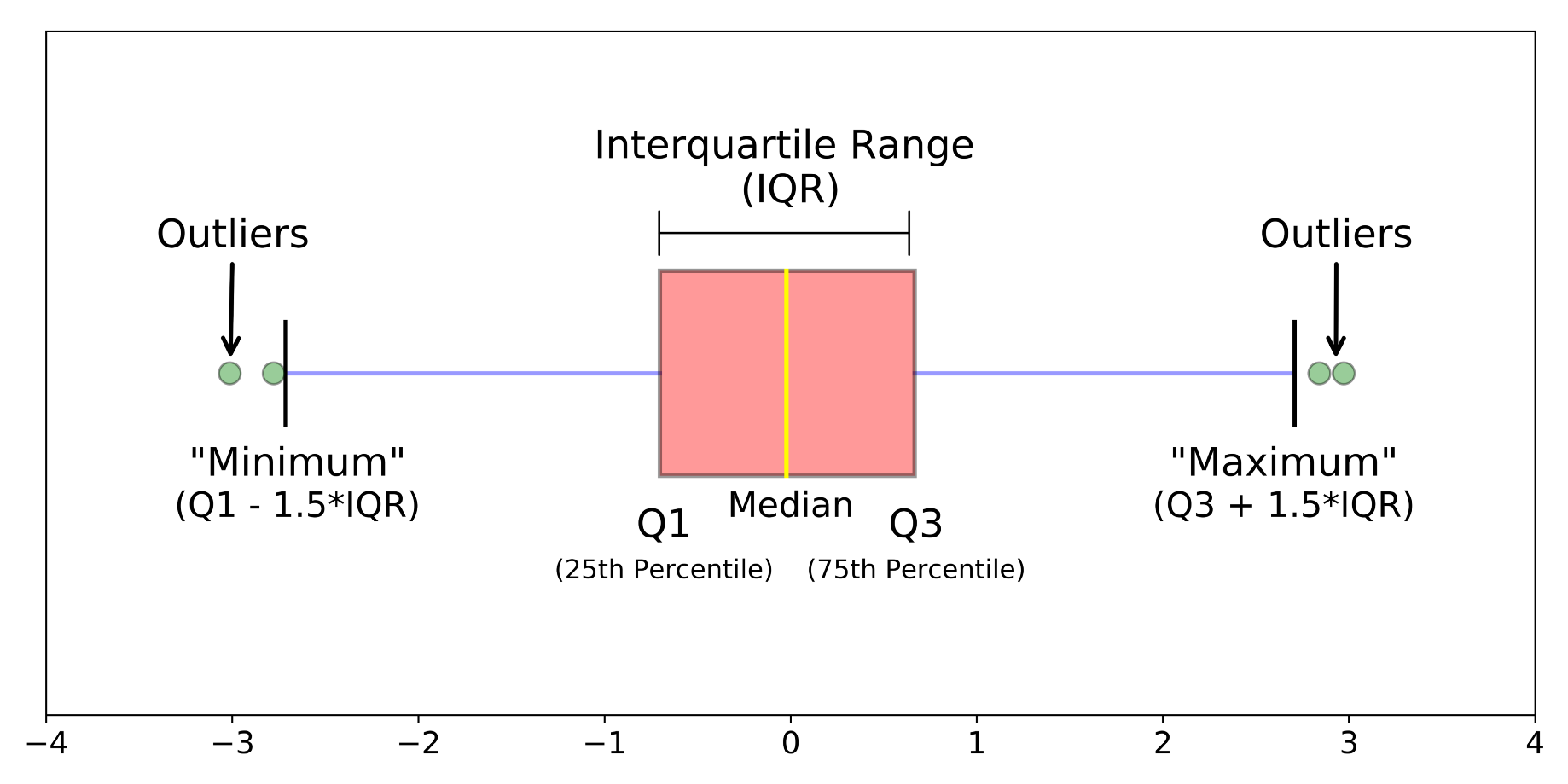
Minimal Ranking
The underside score, excluding outliers (confirmed on the end of the left whisker).
Lower Quartile
Twenty-five p.c of scores fall beneath the lower quartile value (additionally known as the first quartile).
Median
The median marks the mid-point of the data and is confirmed by the street that divides the sector into two components (sometimes known as the second quartile). Half the scores are larger than or equal to this value, and half are a lot much less.
Greater Quartile
Seventy-five p.c of the scores fall beneath the upper quartile value (additionally known as the third quartile). Thus, 25% of knowledge are above this value.
Most Ranking
The perfect score, excluding outliers (confirmed on the end of the correct whisker).
Whiskers
The upper and reduce whiskers characterize scores outside the middle 50% (i.e., the lower 25% of scores and the upper 25% of scores).
The Interquartile Differ (or IQR)
The sector plot displays the middle 50% of scores (i.e., the differ between the twenty fifth and seventy fifth percentile).
Why are subject plots useful?
Discipline plots divide the data into sections containing roughly 25% of the data in that set.
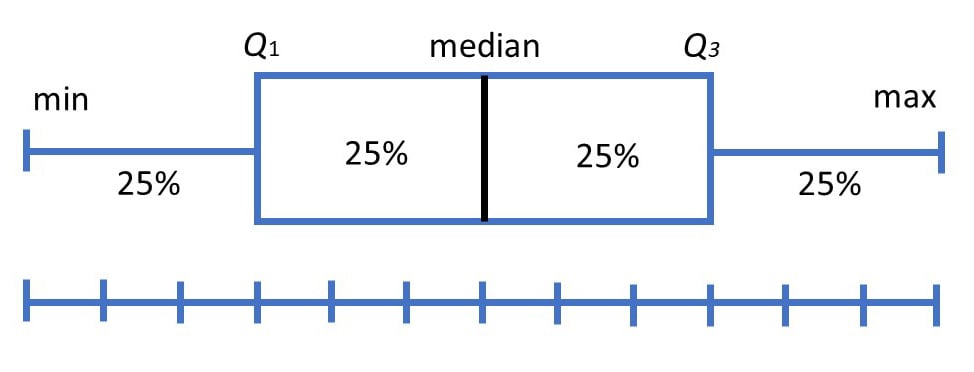
Discipline plots are useful as they provide a visual summary of the data enabling researchers to shortly decide suggest values, the dispersion of the data set, and indicators of skewness.
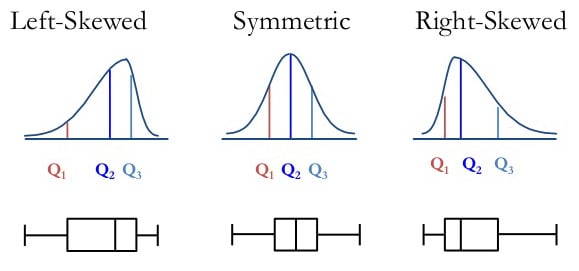
Discover that the image above represents data that has a perfect common distribution, and most subject plots will not conform to this symmetry (the place each quartile is analogous measurement).
Discipline plots are useful as they current the everyday score of an info set
The median is the everyday value from a set of knowledge and is confirmed by the street that divides the sector into two components. Half the scores are larger than or equal to this value, and half are a lot much less.
Discipline plots are useful as they current the skewness of an info set
The sector plot kind will current if a statistical data set is commonly distributed or skewed.
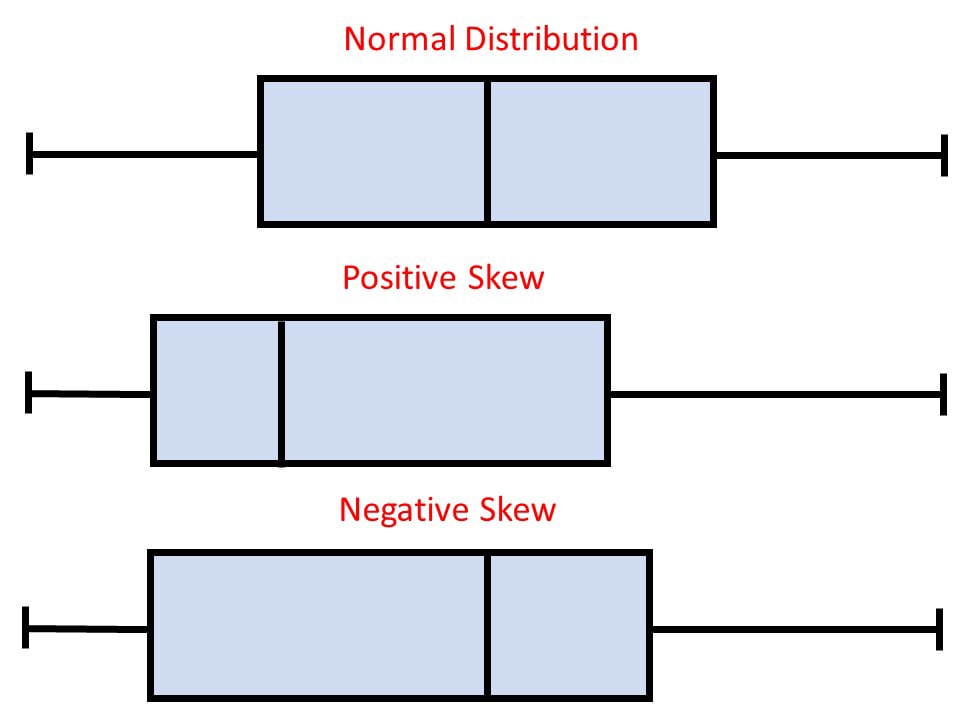
When the median is within the midst of the sector, and the whiskers are concerning the an identical on both facet of the sector, then the distribution is symmetric.
When the median is nearer to the underside of the sector, and if the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the sector, then the distribution is positively skewed (skewed correct).
When the median is nearer to the best of the sector, and if the whisker is shorter on the upper end of the sector, then the distribution is negatively skewed (skewed left).
Discipline plots are useful as they current the dispersion of an info set
In statistics, dispersion (moreover generally known as variability, scatter, or unfold) is the extent to which a distribution is stretched or squeezed.
The smallest and largest values are found on the end of the ‘whiskers’ and are useful for providing a visual indicator regarding the unfold of scores (e.g., the differ).
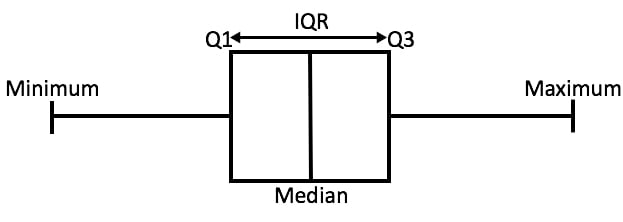
The interquartile differ (IQR) is the sector plot exhibiting the middle 50% of scores and could be calculated by subtracting the lower quartile from the upper quartile (e.g., Q3−Q1).
Discipline plots are useful as they current outliers inside an info set
An outlier is an commentary that is numerically distant from the rest of the data.
When reviewing a subject plot, an outlier is printed as an info stage that is located outside the whiskers of the sector plot.
Provide: https://towardsdatascience.com/understanding-boxplots-5e2df7bcbd51
As an illustration, outside 1.5 cases the interquartile differ above the upper quartile and beneath the lower quartile (Q1 – 1.5 * IQR or Q3 + 1.5 * IQR).
The way in which to judge subject plots
Discipline plots are a useful choice to visualise variations amongst utterly totally different samples or groups. They deal with to supply a wide range of statistical information, along with — medians, ranges, and outliers.
Discover although subject plots have been provided horizontally on this text, it is additional widespread to view them vertically in evaluation papers.
Step 1: Study the medians of subject plots
Study the respective medians of each subject plot. If the median line of a subject plot lies outside of the sector of a comparability subject plot, then there’s extra more likely to be a distinction between the two groups.
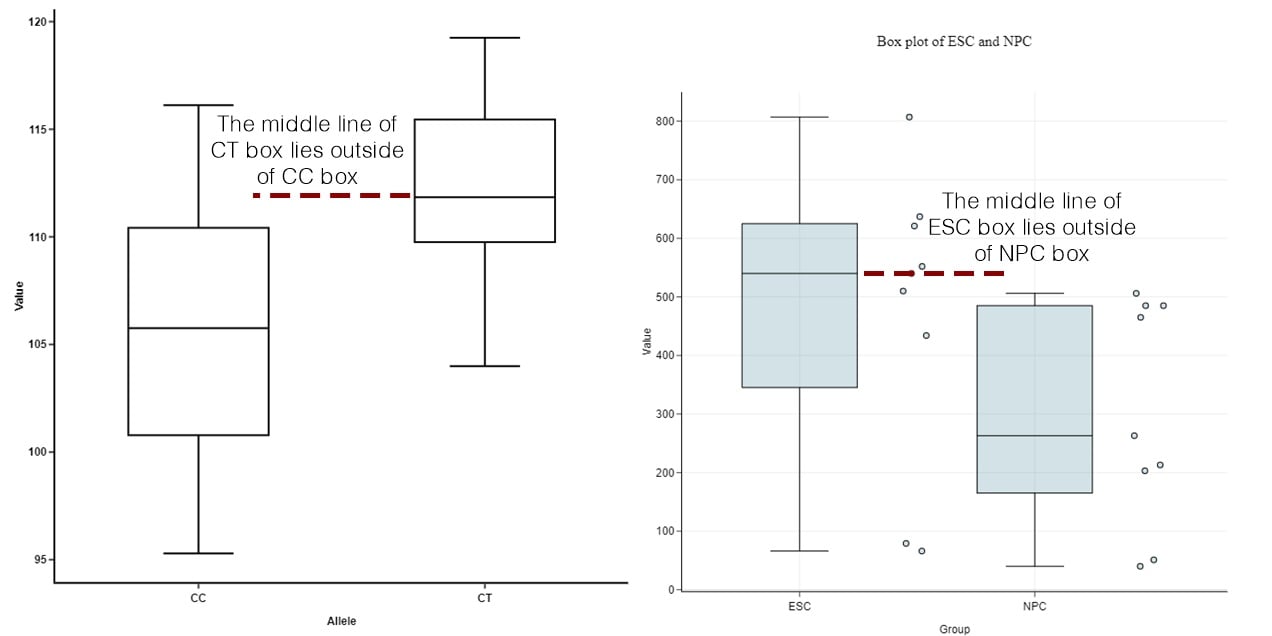
Provide: https://weblog.bioturing.com/2018/05/22/how-to-compare-box-plots/
Step 2: Study the interquartile ranges and whiskers of subject plots
Study the interquartile ranges (that is, the sector lengths) to have a look at how the data is dispersed between each sample. The longer the sector, the additional dispersed the data. The smaller, the a lot much less dispersed the data.
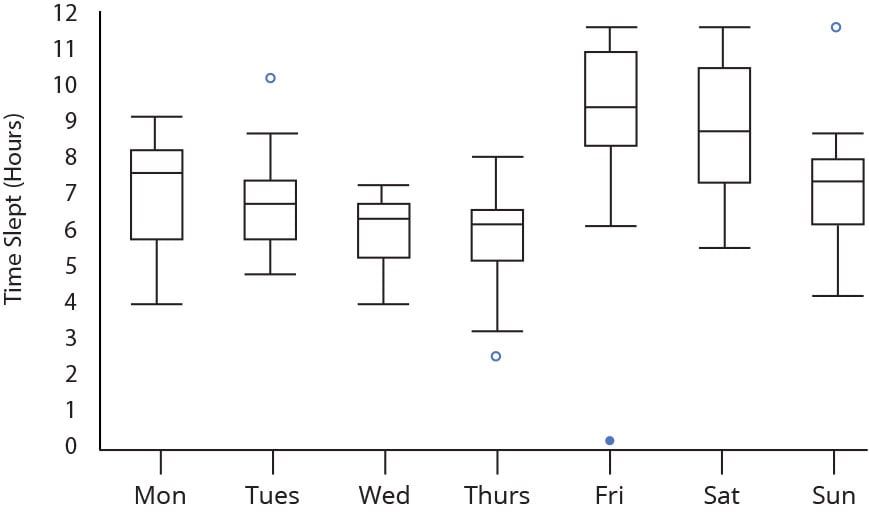
Subsequent, take a look on the common unfold as confirmed by the extraordinary values on the end of two whiskers. This displays the differ of scores (one different form of dispersion). Larger ranges level out wider distribution, that is, additional scattered data.
Step 3: Seek for potential outliers (see the above image)
When reviewing a subject plot, an outlier is printed as an info stage that is located outside the whiskers of the sector plot.
Step 4: Seek for indicators of skewness
If the data do not seem like symmetric, does each sample current the an identical form of asymmetry?