Iconic memory is the seen sensory memory register which retailers seen pictures after the extinction of a bodily stimulus. Whereas iconic memory incorporates an infinite functionality, it declines shortly.
Information saved in iconic memory usually disappears inside half a second (counting on the brightness).
Iconic memory is a sensory memory half involving a fast-decaying seen information retailer (Sperling, 1960). It provides a coherent however fleeting illustration of our seen notion (Pratte, 2018).
Aristotle was among the many many earliest individuals to have documented the persistence of a visual illustration of an object following its bodily extinction (Allen, 1926). He recognized that experiencing a dream entails afterimages.
Inside the 18th and nineteenth centuries, observing the trail of sunshine engendered by a shifting stick’s shining ember elicited the curiosity of many researchers. They delved into the empirical analyses of this phenomenon which was subsequently described as seen persistence (Coltheart, 1980).

In the end, in 1960, the American cognitive psychologist George Sperling, by means of quite a few experiments, confirmed functionality and interval as parts of a memory system referred to as seen sensory memory (Sperling, 1960).
Seven years later, Ulric Neisser launched the time interval ‘iconic memory’ to seek the advice of with this fast-decaying retailer of memory (Neisser, 1967).
In keeping with the current understanding of iconic memory, informational persistence and visual persistence embody mainly distinct properties, and the earlier is believed to significantly contribute to seen short-term memory (Coltheart, 1980; Irwin & Yeomans, 1986).
Examples of Iconic Memory
Following are some examples of iconic memory:
- You briefly survey the objects in your mattress room sooner than turning the lights off. The memory of how your surroundings appeared is an occasion of iconic memory.
- You cross an infinite billboard whereas driving on the freeway. Your memory of what you observed on the billboard is an occasion of iconic memory.
- Whereas utilizing on the apply, you see a lamb grazing inside the meadows. The memory of what you briefly beheld is an occasion of iconic memory.
- You are exterior on a darkish and moist night time time. The entire sudden, your surroundings are lit up by a flash of lightning. The fleeting image you observed beneath the transient glow, which you’ll be able to subsequently recall, is an occasion of iconic memory.
Sperling’s Experiments
In his preliminary experiments carried out in 1960, Sperling launched the observers with a tachistoscopic stimulus comprising quite a few alphanumeric characters for virtually 50 milliseconds (Sperling, 1960).
Afterward, based totally on a cue, the members wanted to recall strains of letters from the present. The effectivity of memory was in distinction beneath whole report and partial report circumstances.
What was the excellence between Sperling’s full report and partial report duties?
Whereas the “whole report” required the members to recall parts consistent with their distinctive spatial positions, the “partial report” demanded that subsets of the present’s characters be acknowledged based totally on cued recall at utterly totally different time intervals. A extreme, medial, or low tone would level out which group of characters wished to be reported.
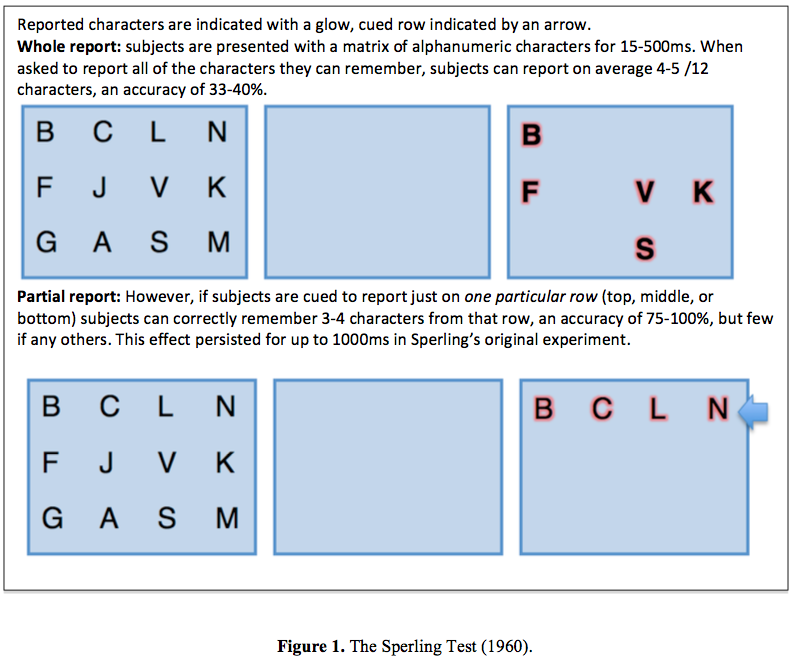
Under your entire report circumstances, the members have been usually able to recall about 35% of the characters on present (Sperling, 1960). The findings counsel that your entire report is restricted by a system of memory that has a functionality of 4 to 5 objects.
Nevertheless, beneath the partial report circumstances, the members might recall a selected row in 75% of the trials.
Because of the members have been unaware of the row that they need to recall, the effectivity herein was tantamount to a random sampling of the memory of the members to your full present.
The outcomes herein appeared to counsel that three-fourths of the seen present remained accessible to memory. This finish outcome signified a manifest improve in iconic memory’s hypothesized functionality.
Iconic Memory and Change Blindness
Change blindness is the phenomenon whereby an alteration launched to the seen stimulus escapes the uncover of the observer (Becker, Pashler & Anstis, 2000). The transient interval between the two successive seen scenes, the latter of which is barely altered, is named the interstimulus interval.
The scale of the interstimulus interval is believed to chop again the long-lasting memory retailer. In numerous phrases, iconic memory is what permits the detection of modifications in a visual scene (Persuh, Genzer & Melara, 2018).
Nonetheless, lapses in iconic memory, which may very well be outlined as change blindness, usually tend to occur in proportion to the dimensions of the interstimulus interval.
Neurology Related to Iconic Memory
The retina’s photoreceptors, the retinal ganglion cells, the middle occipital gyrus, proteins inside the thoughts and quite a few genetic parts have an effect on the functioning of iconic memory.
The seen sensory pathway performs a big perform in iconic memory. The retina’s photoreceptors, particularly rods, and cones, keep energetic previous a stimulus’ bodily offset (Irwin & Thomas, 2008). The transient M-type cells and the sustained P-type cells of the retinal ganglion cells are moreover involved (Levick & Zacks, 1970).
Whereas the earlier are energetic solely all through stimulus onset and offset, the latter are energetic even in between. The primary seen cortex all through the occipital lobe, too, performs a vital perform inside the course of (Nikolić, Häusler, Singer & Maass, 2009).
Moreover, the middle occipital gyrus shapes iconic memory’s functionality to detect change (Beste, Schneider, Epplen & Arning, 2011). Proteins inside the thoughts and quite a few genetic parts moreover have an effect on iconic memory’s functioning.
Key Takeaways
- Iconic memory is a sensory memory that retailers pictures for a fraction of a second.
- Iconic memory permits for the retention of seen sensory impressions following the cessation of the distinctive stimulus, with the tip outcome {{that a}} seen stimulus is subjectively sustained by as a lot as quite a few hundred
milliseconds. - In 1960 George Sperling demonstrated that, for a brief interval following the termination of a 50-millisecond present of letters, additional information was on the market than an observer might often report.
- Future analysis have centered on the outcomes of luminance, interval, distinction, and background diploma on the readability and interval of iconic memory storage.
FAQs
What does iconic memory retailer?
Iconic memory retailers seen information from the setting, allowing for transient and short-term retention of seen stimuli. It is accountable for holding a visual snapshot of the sensory enter sooner than extra processing and interpretation occur.
What is the interval of iconic memory?
The interval of iconic memory could also be very transient, often lasting for a fraction of a second to some seconds. It is a fleeting and transient sort of memory that provides a short-lived illustration of seen information sooner than it quickly decays or is overwritten by new incoming stimuli.
References
Allen, F. (1926). The persistence of imaginative and prescient. American Journal of Physiological Optics, 7, 439–457.
Becker, M. W., Pashler, H., & Anstis, S. M. (2000). The perform of iconic memory in change-detection duties. Notion, 29 (3), 273-286.
Beste, C., Schneider, D., Epplen, JT, & Arning, L. (2011). The purposeful BDNF Val66Met polymorphism impacts options of pre-attentive seen sensory memory processes. Neuropharmacology, 60 (2-3), 467-471.
Coltheart, M. (1980). Iconic memory and visible persistence. Notion & psychophysics, 27 (3), 183-228.
Dick, A. O. (1974). Iconic memory and its relation to perceptual processing and totally different memory mechanisms. Notion & Psychophysics, 16 (3), 575-596.
Irwin, D. E., & Yeomans, J. M. (1986). Sensory registration and informational persistence. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Notion and Effectivity, 12 (3), 343.
Irwin, D. E., & Yeomans, J. M. (1986). Sensory registration and informational persistence. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Notion and Effectivity, 12(3), 343.
Irwin, D., & Thomas, L. (2008). Neural basis of sensory memory. Seen memory32-35.
Levick, W. R., & Zacks, J. L. (1970). Responses of cat retinal ganglion cells to transient flashes of sunshine. The Journal of Physiology, 206 (3), 677-700.
Neisser, Ulric (1967). Cognitive Psychology. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Nikolić, D., Häusler, S., Singer, W., & Maass, W. (2009). Distributed fading memory for stimulus properties inside the main seen cortex. PLoS biology, 7 (12), e1000260.
Persuh, Marjan; Genzer, Boris; Melara, Robert (20 April 2018). Iconic memory requires consideration. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 6126.
Pratte, M. S. (2018). Iconic recollections die a sudden demise. Psychological science, 29 (6), 877-887.
Sperling, G. (1960). The info on the market briefly seen shows. Psychological monographs: Frequent and utilized, 74 (11), 1.
Extra Finding out
